What is a SSL Certificate; Do I need one?
If you are reading this, then you've undoubtedly seen the term 'SSL Certificate' or just 'SSL' mentioned somewhere or other in the past few months, and you might be wondering - what is an SSL Certificate, and should my website or application have one?
SSL Certificate stands for Secure Socket Layer Certificate, which is a file that allows your website or application to create encrypted and secure connections to your users. Websites using SSL can be identified by the prefix 'https' in their URL (the 's' stands for Secure); Your browser will typically display a green lock icon or turn the URL bar green when visiting these sites.
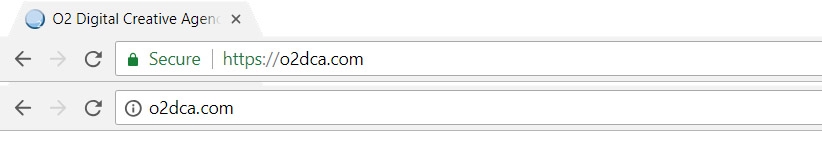
Example of Chrome's address bar with a secure (top), and insecure (bottom) URL
One of the most common ways for hackers to steal information, and marketing companies to track users, is to intercept the data sent when they are browsing the web - this is commonly called 'sniffing'. Sniffing can easily be done on a non-SSL connection with free software - so easily, that airports, coffee shops, any public wifi you use is almost definitely intercepting your traffic to some degree, if only to serve you better advertisements. SSL negates this vulnerability by creating a secure connection to a website, such that only the website, and your computer can understand the information being sent back and forth. So - do you need a SSL certificate? If your website has any type of form, or deals with any payment transactions, you're going to want an SSL certificate. Even a simple contact form should be secured with SSL to prevent a 3rd party from intervening. If your website doesn't have any of those - there is still a valid reason to have an SSL certificate: Google is using it as a search ranking parameter. This means that sites with an SSL certificate will appear higher in results than sites without one (https://webmasters.googleblog.com/2014/08/https-as-ranking-signal.html).
SSL negates this vulnerability by creating a secure connection to a website, such that only the website, and your computer can understand the information being sent back and forth. So - do you need a SSL certificate? If your website has any type of form, or deals with any payment transactions, you're going to want an SSL certificate. Even a simple contact form should be secured with SSL to prevent a 3rd party from intervening. If your website doesn't have any of those - there is still a valid reason to have an SSL certificate: Google is using it as a search ranking parameter. This means that sites with an SSL certificate will appear higher in results than sites without one (https://webmasters.googleblog.com/2014/08/https-as-ranking-signal.html).
 Pure Oxygen
Pure Oxygen
There are no published comments.
New comment